What is 5G? Everything You Need To Know
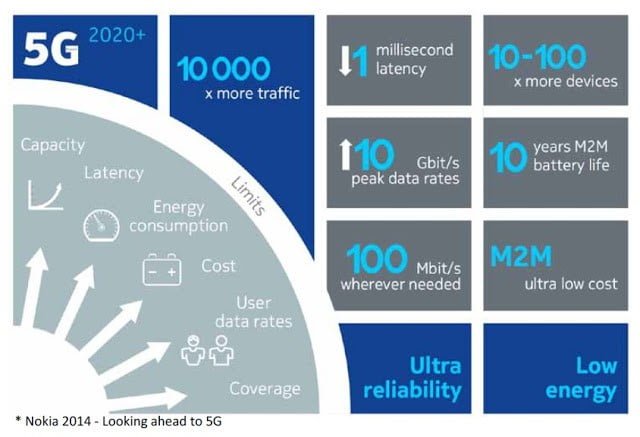
5G is the fifth generation of cellular mobile communications. It succeeds the 4G (LTE/WiMax), 3G(UMTS) and 2G (GSM) systems. 5G performance targets high data rate, reduced latency, energy saving, cost reduction, higher system capacity, and massive device connectivity.
5G networks are expected to launch across the world by 2020. Everyone wants higher internet speed.

Interesting Specifications Of 5G
• Faster download and upload speeds
• Smoother streaming of online content
• Higher-quality voice and video calls
• More reliable mobile connections
• Greater number of connected IoT (Internet of Things) devices
• An expansion of advanced technologies – including self-driving cars and smart cities.
New Radio
5G NR (New Radio) as its 5G communication standard proposal. 5G New Radio can include lower frequencies, from 600 MHz to 6 GHz.
It will push mobile speeds from 100 Mbps to upward of 10 Gbps, a huge increase that will make next-generation wireless competitive with even the fastest fiber-optic wired networks.

Fifth Generation will run on a new “high-spectrum band” which uses higher frequency signals than 4G. The new band will be much less congested than at present. However, signals won’t be able to travel as far, so there will need to be more access points positioned closer together.
“5G” antennas are expected to be smaller, more numerous and part of more high-gain systems than those that have served 3G and 4G systems, and they will need more advanced steering and scanning techniques in order to function well at millimeter wave frequencies.
Smartphone brands are ready to launch their 5G ready smartphone next year including Xiaomi, Oneplus, Samsung, Oppo, Huawei.
Ultra Low Latency
5G’s ultra-low-latency could range between 1ms and 10ms. This would enable, for example, a spectator in a football stadium to watch a live stream of an alternative camera angle of the action that matches what is going on the pitch ahead with very little delay. That will also open the door for VR and AR in real-time. 4G is capable of between 40ms and 60ms, which is not always enough to provide a real-time response.
Latency is the response time between when you click on a link or start streaming a video on your phone, sending the request up to the network, and when the network responds and gives you your website or starts playing your video.
With 5G, that latency gets reduced to as little as 1 millisecond, or about the time it takes for a flash in a normal camera to finish.
Small cell
Traditional cellular coverage typically stems from gigantic towers littered with different radios and antennas. Those antennas are able to broadcast signals at a great distance, so you don’t need a lot of them. Small cells are the opposite — backpack-size radios can be hung up on street lamps, poles rooftops or other areas. They can only broadcast a 5G signal at a short range, so the idea is to have a large number of them in a densely packed network.
Applications
• Ultra fast mobile internet
• High performance, HD multimedia download and streaming
• Internet of Things applications
• Healthcare and wearable applications
• Mission critical applications
• Autonomous driving and position mapping
• Industrial automation and real time monitoring
• Smart sensor technology for agriculture and farming
• Inventory management, warehouse and shipping
• Smart city and security applications





