Solid Waste in India

India is having the second largest population in the world after China with more than 1.27 billion population contributing 17.6% of the world’s total population (Official population clock). On the contrary, India is sharing only 5% of world’s area accounting for 3,185,263 km. Out of the total population, 68% live in rural areas, while 32% lives in urban areas (WorldBank, 2014). The urban population is increasing day by day for last few decades. In modern society, industry becomes an essential part. Developing countries like India is in the industrialization phase, which also contribute to urbanization. Large number of people are migrating towards city area for better opportunities. In terms of GDP, India is one of the fastest-growing economies in the world with 7.30% GDP. It is expected that by 2030 India will be growing with GDP of 10%. Higher GDP will result in improved living standards.
- 7.2 million tonnes of hazardous waste
- One Sq km of additional landfill area every-year
- Rs 1600 crore for treatment & disposal of these wastes
- In addition to this industries discharge about 150 million tonnes of high-volume low hazard waste every year, which is mostly dumped on open low-lying land areas.
Growth of Solid Waste In India
- Waste is growing by leaps & bounds
- In 1981-91, population of Mumbai increased from 8.2 million to 12.3 million
- During the same period, municipal solid waste has grown from 3200 tonnes to 5355 tonne, an increase of 67%
- City like Bangalore produces 2000 tonnes of waste per annum.
- Waste collection is very low for all Indian cities
How solid waste affected us in recent years?
- In Mumbai (2005) clogged the sewage line due to large no. of plastic bags.
- Blast in the Bhusan Steel factory at Noida,
- Reduction in the number of migratory birds due to consumption of contaminated foods
- animals dying on streets and farmland due to the consumption of plastic bags, which blocks the food movement in their stomach
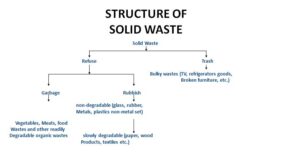
- It is defined as “non-liquid, non-soluble materials ranging from municipal garbage to industrial wastes that contain complex & sometimes hazardous substances”
- Solid waste also includes Garbage, Rubbish, Demolition products, Sewage treatment residue, Dead animals, Manure and other discarded material.
Source
- Agriculture
- Fisheries
- Household
- Commerce and industry
Effects of solid waste
A: Health hazard
- If solid waste are not collected and allowed to accumulate, they may create unsanitary conditions.
- This may lead to epidemic outbreaks.
- Many diseases like cholera. Diarrhea, dysentery, plague, jaundice, or gastro-intestinal diseases may spread and cause loss of human lives.
- In addition improper handling of the solid wastes, is a health hazard for the workers who come in direct contact with the waste.
B: Environmental impact
- If the solid wastes are not treated properly decomposition and putrefaction( decay) may take place.
- The organic solid waste during decomposition may generate obnoxious (intolerable odor)
Solid Waste management is the
- Collection
- Storage
- transport and handling
- recycling
- disposal and monitoring of waste materials.
Collection of municipal solid waste
Littering of municipal solid waste shall be prohibited in cities, towns and areas notified by the government
To prohibit littering, the following steps shall be taken to collect the waste
1. Organizing house-to-house collection of garbage through any of the methods like containerized collection, community bin collection (Central bin), House to house collection, collection at regular pre-informed timings and scheduling by using ringing bells/musical vehicles (without exceeding the permissible noise levels)
2. Collection of waste from slums and squatter areas/localities including hotels/ restaurants/office complexes and commercial areas shall be devised in consultation with municipal authority.
3. Fruits and vegetable market waste which are bio-degradable in nature shall be managed to make use of such waste
4. Biomedical waste and industrial waste shall not be mixed with municipal solid waste as per rules specified separately for the purpose
5. Collected waste from the residential and other areas shall be transferred to community bins or dhalaos by hand-driven containerized carts
6. Horticultural and construction/demolition waste wastes /debris waste shall be separately collected and disposed off following proper norms. Similarly, activities relating to dairies (milking of cows/buffaloes) shall be regulated in accordance with state laws.
- Waste (garbage, dry leaves)shall not be burnt.
- Stray animals should not be allowed to move around waste storage facilities.
Storage of municipal solid waste
Galvanized steel dust bin and Public bins
Storage
Municipal Authorities shall establish and maintain storage facilities in such manner as not to create unhygienic/insanitary conditions around it. Following criteria shall be taken into account while establishing and maintaining storage facilities ;
1. Storage facilities shall be created /established by taking into account quantities of waste generation in a given area and the population density
2. Storage facilities to be set up by the municipal authority or by any other agency shall be so designed that waste stored is not exposed to open atmosphere and shall be aesthetically acceptable and user-friendly.
- Storage facilities or bins shall have easy to operate design for handling, transfer and transportation of waste
4. Manual handling of waste shall be prohibited. If unavoidable due to constraints, manual handling shall be carried out under proper precaution with due care for the safety of workers
Transportation of municipal solid waste

Vehicles used for transportation of wastes shall be covered, wastes should not be visible to public, nor exposed to open environment. The following criteria shall be met;
- The storage facilities set by the municipal authorities shall be daily attended for clearing of wastes
- Collection and transportation vehicles shall be so designed that multiple handling of wastes, prior to final disposal, is avoided
Disposal of municipal solid waste
1. Dumping
2. landfill
3. Controlled Tipping or Sanitary Landfill
4. Incineration
5. Composting
6. Pyrolysis






